应用于动脉和内脏大出血的止血材料要求具有良好的止血性能、湿态组织粘附性以及力学性能。本研究将壳聚糖(CS)与丝素蛋白(SF)通过单宁酸(TA)交联制备出结构稳定的水凝胶,其可以实现各种脏器出血模型在短时间内止血。本研究制备的水凝胶作为一种优良的止血密封剂,在急性创面和大出血情况下具有显著的优势。
一、论文信息
该论文共同第一作者为清源创新实验室生物分析与纳米医学科研团队成员、福州大学乔紫雯、福州大学吕雪丽、福建省立医院小儿外科主任医师何少华。通讯作者为清源创新实验室生物分析与纳米医学科研团队负责人、福州大学杨黄浩教授及团队成员张进教授、中科院长春应化所丁建勋教授。
论文以“A mussel-inspired supramolecular hydrogel with robust tissue anchor for rapid hemostasis of arterial and visceral bleedings”为题,发表于在Materials Science,Biomaterials领域排名第一的高质量英文期刊Bioactive Materials(DOI:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.01.039)。

二、研究内容
研究人员制备了一种10s内即可完成超分子交联过程的生物可降解CS/TA/SF水凝胶,并将其应用于大鼠、兔各种大出血模型的快速止血。CS/TA/SF水凝胶的超交联网络,是由CS支链中的氨基/羟基、SF中的酰胺基与TA中的酚羟基分别形成氢键而构成的。TA作为一种天然的生物分子基粘合剂,对蛋白质具有较高的结合力,使得CS/TA/SF水凝胶能够与湿组织形成可逆的强相互作用。引入的CS组分可以加快血液吸收、并且具有良好的凝血能力和高的红细胞粘附性,进一步促进了大动脉止血的效率(示意图1)。
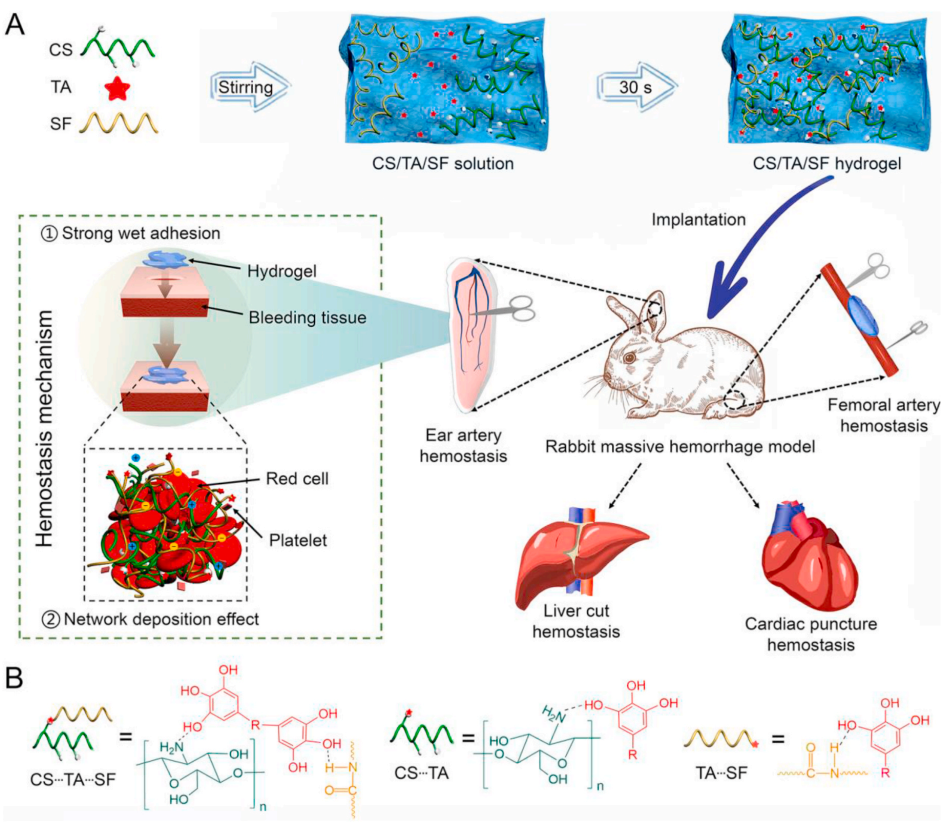
Scheme 1. Schematic illustration of (A) preparation and (B) cross-linking-network structure of CS/TA/SF hydrogel for massive arterial and visceral hemorrhage.
如图1所示,CS/TA/SF超分子水凝胶微观形貌呈现多孔结构,具有出色的机械性能,包括拉伸强度、杨氏模量和断裂伸长率。这主要是由于CS/SF优异的延展性和CS/TA/SF三组分超分子交联网络的存在。另一方面,CS/TA/SF凝胶在接触角实验中展现出优越的亲水性和吸湿性,主要归因于CS是一种亲水性聚合物,含有许多羟基(−OH)和胺(−NH2)基团,而含酚羟基的TA也具有高度亲水性,在水中表现出良好的溶解性。此外,高度交联度CS/TA/SF水凝胶含有的稳定多孔结构有利于气体(O2和CO2)交换,吸收来自损伤表面的渗出物并抑制渗出物积聚,最终把伤口部位的有害影响降到最低。
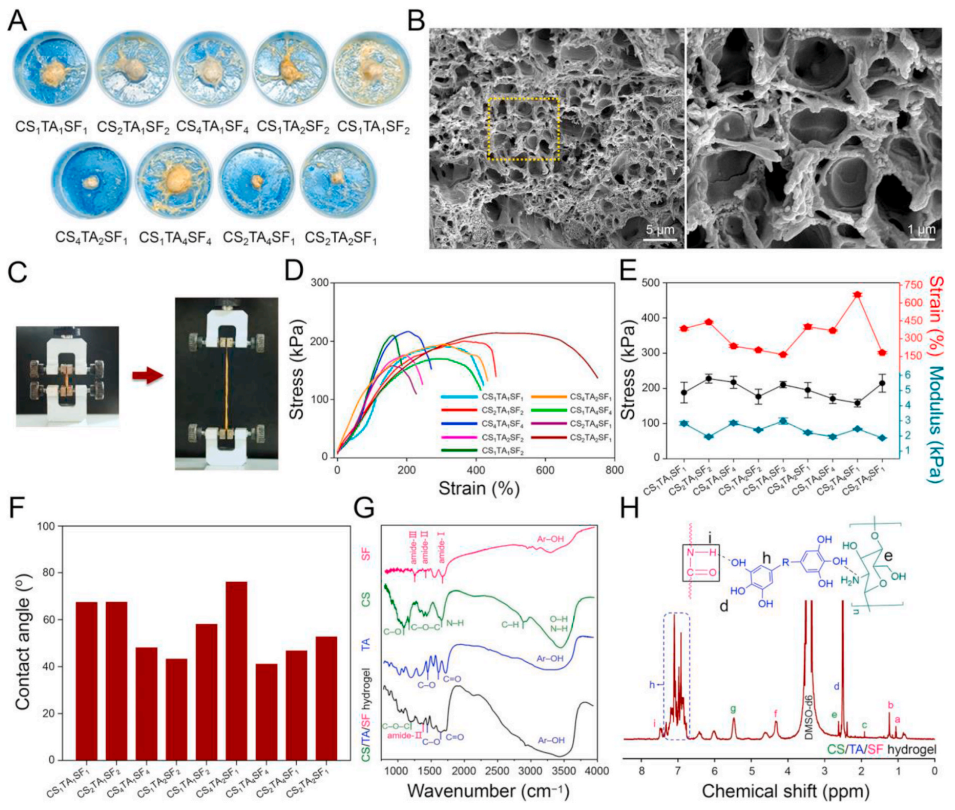
Fig. 1. Structural and physical properties of CS/TA/SF hydrogels with different weight ratios. (A) Photographs showing gross morphologies of hydrogels onto polypropylene dish. (B) SEM images of hydrogel after lyophilization. Right is the higher magnification image of the retangular area in the left one. (C) Tensile testing photograph of hydrogel. (D) Representative tensile stress− strain curves. (E) Comparison of tensile strength, strain, and Young’s modulus of hydrogels with different weight ratios. (F) Contact angles for water droplet on hydrogel surface. (G) Conformational analysis of hydrogel by FTIR spectroscopy. (H) 1 H NMR spectra of hydrogel. All statistical data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3; ***P < 0.001).
理想的止血材料应具有湿态强黏附作用,以促进快速凝血,减少失血。基于此,研究人员们通过对9组不同组分比例的CS/TA/SF水凝胶进行止血效果评价后,再分别检验其对湿组织的剪切黏附能力。在该体系中,一方面TA通过静电作用和氢键与SF、CS中的氨基酸结合,维持了CS/TA/SF水凝胶的结构稳定性;另一方面,水溶性TA含有亲水性多酚,其末端不仅能通过氢键进行自组装聚集,还可与蛋白质和肽等生物分子紧密结合,保证了CS/TA/SF水凝胶超强的湿组织粘附性。这种超分子网络结构对于吸收伤口渗出物、阻断红细胞和血小板作为止血剂的逃逸至关重要。如图2所示,CS/TA/SF水凝胶的止血机理,主要是通过CS与红细胞表面的阴离子相互作用形成阳离子团簇,从而诱导血小板聚集。其中,CS能被范德华力、静电力、氢键等非特异性作用力吸附在细胞表面,加速血液流动,加快红细胞凝血。并且,SF和TA与血小板和凝血因子的直接相互作用加速了血栓的形成,这三种材料的共聚进一步发挥了正向的协同止血作用。
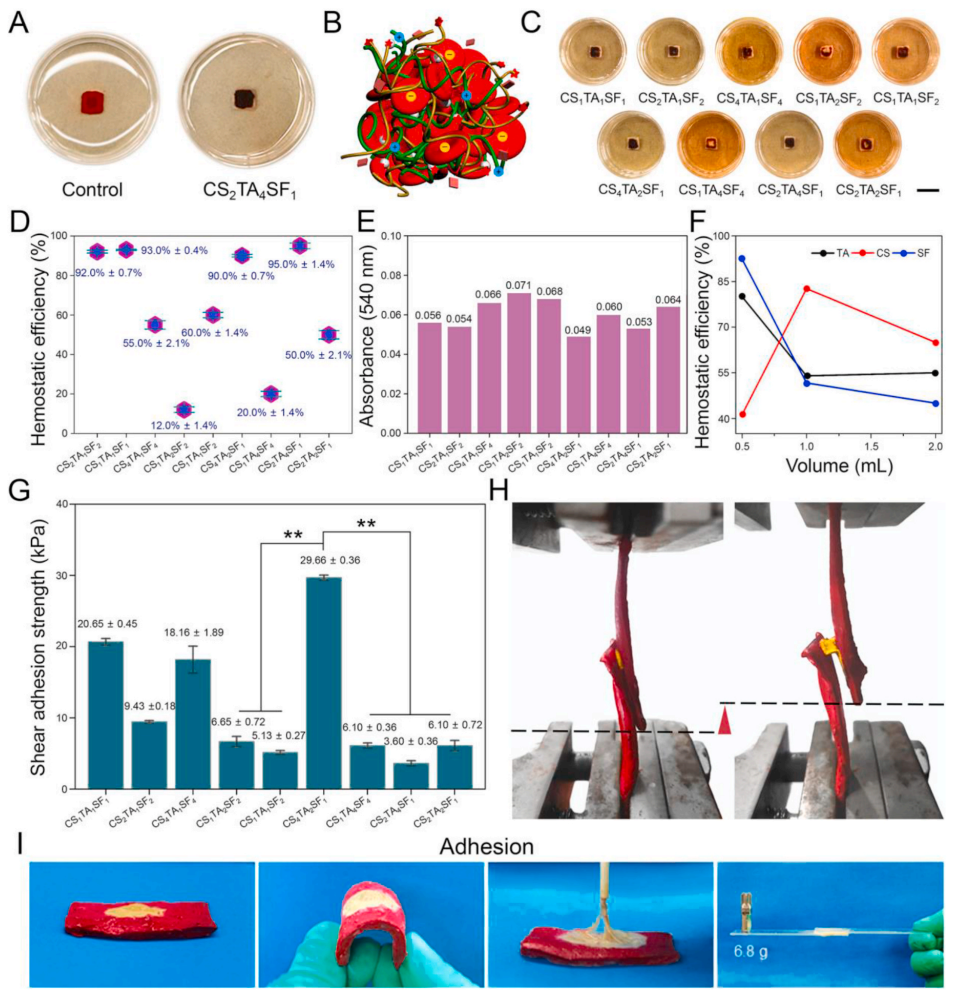
Fig. 2. Hemostatic performance and wet shear adhesion strength of CS/TA/SF hydrogel with different weight ratios. (A) Photographs showing clot formation on hydrogel and polypropylene dish. (B) Schematic illustration of hemostatic mechanism. (C) Photographs showing blood pro-coagulant efficacy of hydrogels (scale bar = 10 mm). (D) Hemostatic efficiency of hydrogels. (E) Absorbance of hemoglobin tested by microplate reader. (F) Changes of hemostatic efficiency with different volume ratios of CS, TA, and SF. (G) Shear adhesion strength of hydrogel using wet porcine skin as substrate. (H) Lap shear testing photographs of hydrogel using an Instron machine 1185. (I) Photographs showing a strong adhesion of hydrogel with wet porcine skin and glass. All statistical data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).
依据正交实验的设计原则,通过单组分水平性分析验证止血材料性能的代表实验,包括机械性能、亲水性、吸湿性、体外止血效率以及生物安全性,最终,确定了最优组分比CS2/TA1/SF1水凝胶的成分配比(图3A−H, J, K)。血液凝固是一个动态的过程,在这个过程中,每一个凝血元件都按一定的顺序有效地进行,并最终将纤维蛋白原转化为纤维蛋白。在本研究中,红细胞被CS2/TA1/SF1水凝胶的胺基聚集,并被超分子网络结构缠结(图3I)。这种CS2/TA1/SF1水凝胶很好地模拟了贻贝足蛋白的化学组成和分级纳米结构,更有利于红细胞的聚集和粘附,为天然止血材料的开发提供了有利前景。
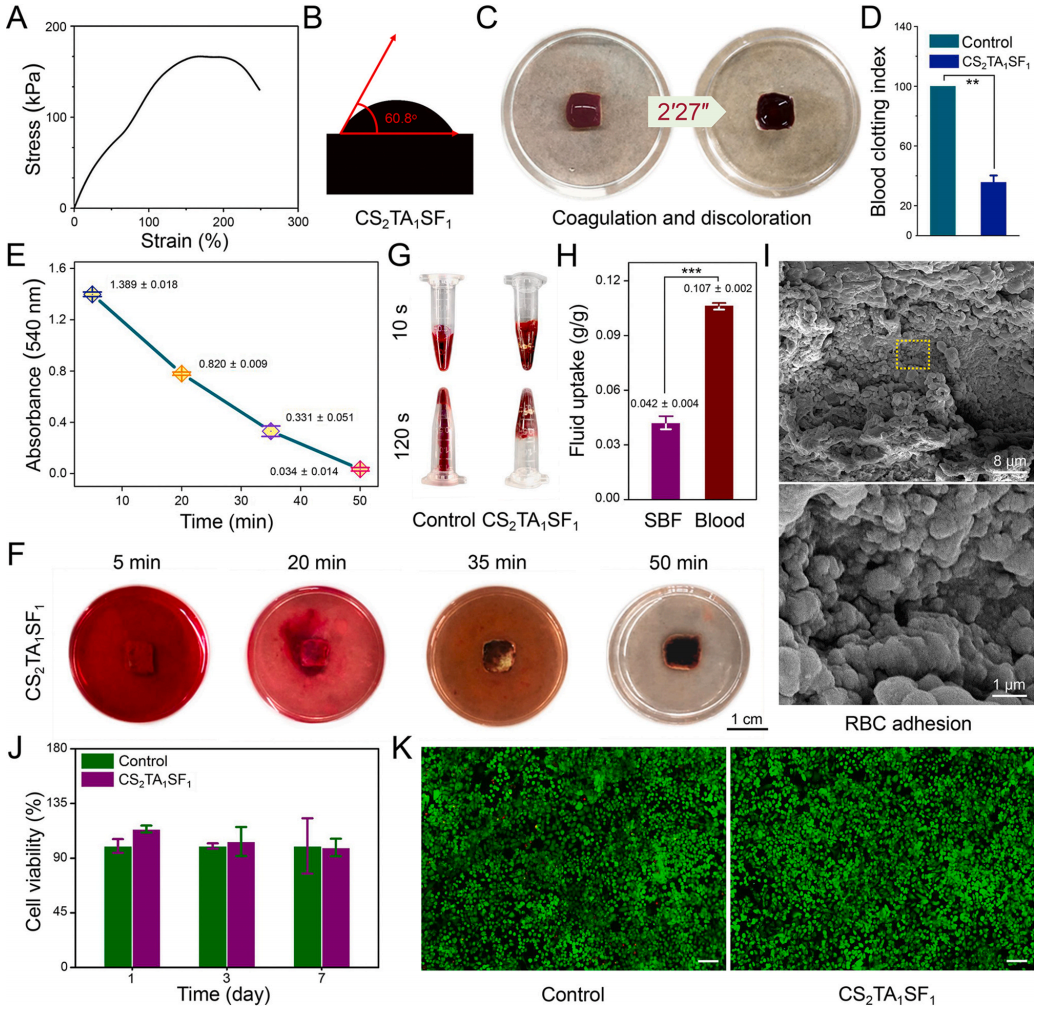
Fig. 3. Comprehensive performance of CS2/TA1/SF1 hydrogel with the optimized weight ratio. (A) Representative tensile stress−strain curve. (B) WCAs measurement. (C) Blood clotting test and (D) BCI of control and sample groups. (E) Whole blood clotting kinetics of hydrogel. (F) Digital photographs of blood absorption kinetics test as a function of time. (G) Photographs of blood coagulation treated with CS/TA/SF hydrogel or nothing. (H) SBF and blood uptake ability of hydrogel. (I) SEM morphologies of RBCs adhesion on hydrogel. Below is the higher magnification image of the retangular area in the above one. (J) CCK-8 assay result of LO2 cells. (K) Live-dead staining images of LO2 cells encapsulated in hydrogel after seven days of incubation (scale bar = 100 μm). All statistical data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3; ***P < 0.001).
为了证明CS2/TA1/SF1水凝胶作为临床止血材料的潜力,将材料用于治疗各种急性组织损伤,包括肝脏、心脏和动脉出血(图4A)。在肝脏上进行快速穿刺和切除止血时,与纱布包缠止血相比较,CS2/TA1/SF1水凝胶通过交联形成封闭剂能立即阻止失血,肉眼观察到快速完成伤口止血。心脏创伤模型中,CS2/TA1/SF1水凝胶能够耐受大鼠心脏跳动的强烈机械扰动,进一步证明了水凝胶的瞬时止血能力和有效的粘附性。测定肝脏、心脏创伤模型出血面积,水凝胶组出血面积仅为未治疗组的1/20,更直观的说明CS2/TA1/SF1水凝胶良好的止血效果(如图4B−C)。
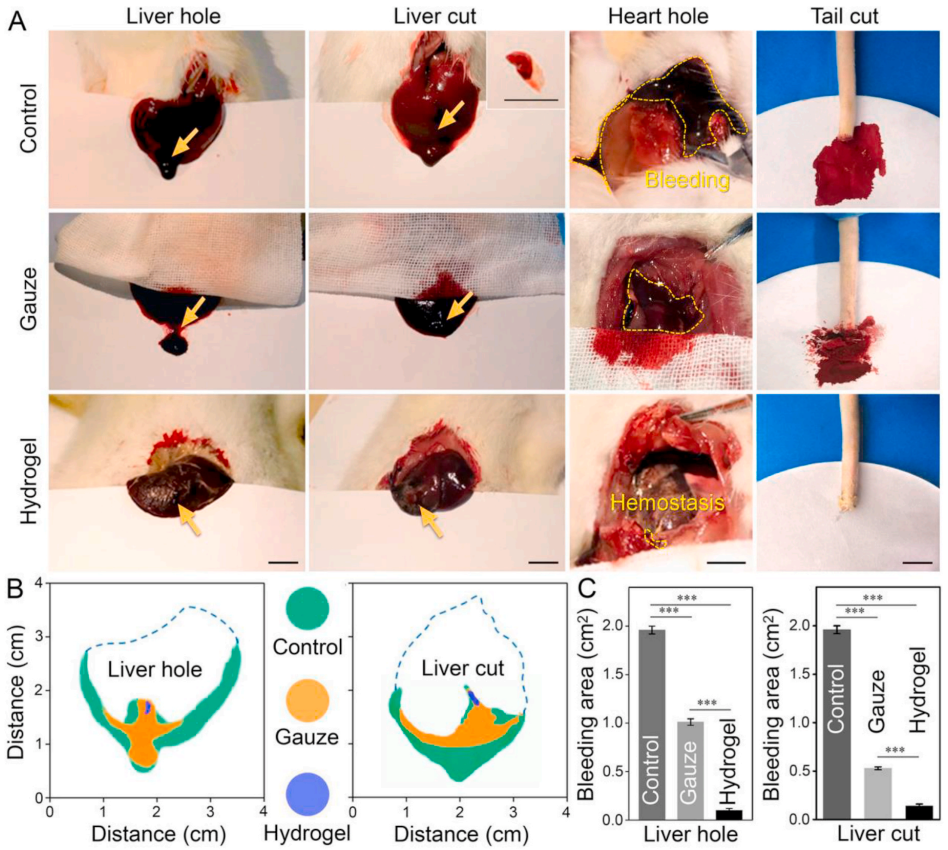
Fig. 4. Hemostatic property of CS2/TA1/SF1 hydrogel in various damage models of rats. (A) Hemostatic images of covering gauze or hydrogel on various wounds with no treatment as a control (scale bar = 1 cm). (B) Comparison of bleeding area in the liver injury model. (C) Quantitative analysis of bleeding area for each group. All statistical data are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3; ***P < 0.001).
构建兔大出血模型,进一步评估了CS2/TA1/SF1水凝胶的止血能力,为将其应用在重大死亡风险的急性大出血损伤提供理论基础。为此,将所研制的机械强度高、血液触发型恢复快、血液摄取量大、血液吸收速度快的注射型CS2/TA1/SF1止血水凝胶应用于兔的耳动脉、肝脏、心脏和股动脉大出血模型(如图5)。有意义的是,在对股动脉损伤模型的研究中,CS2/TA1/SF1水凝胶不仅在动脉血压下可稳定粘附,有效阻止出血,而且,止血后动脉的完整性和血液流动性也得以保留。在术后,CS2/TA1/SF1水凝胶也体现出良好的组织相容性,各项止血效果表明本材料具有优异的快速止血性能,是一种颇有应用前景的天然快速止血材料。
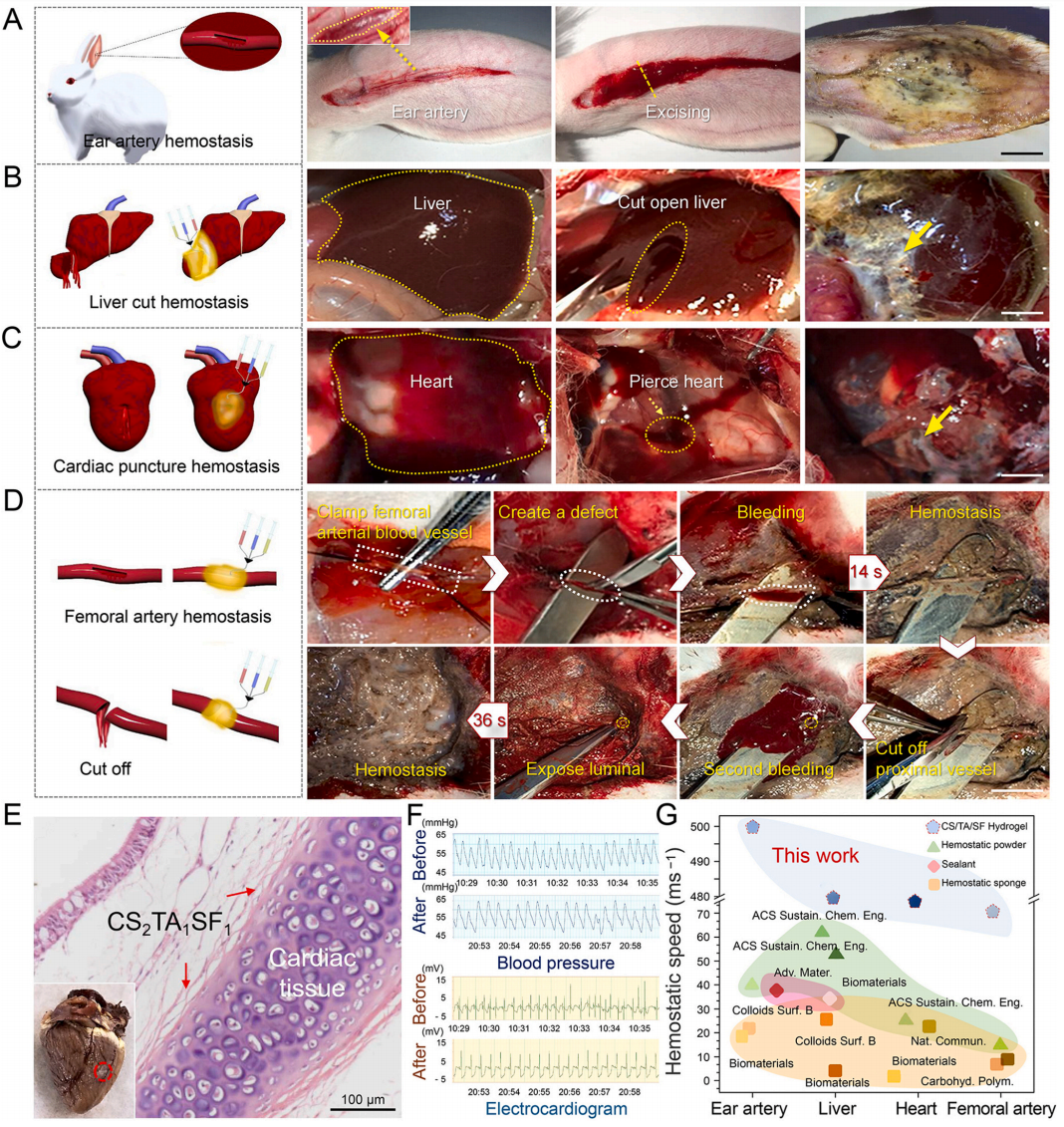
Fig. 5. Hemostatic property and post-operative analysis of CS2/TA1/SF1 hydrogel in various massive hemorrhage models of rabbits. (A) Rabbit ear artery, (B) liver, (C) cardiac puncture, and (D) femoral artery injury models treated by the hemostatic hydrogel (scale bar = 1 cm). (E) Photograph and H&E staining image of interface reaction between rabbit cardiac tissue and hydrogel. (F) MAP through a rabbit's carotid artery and ECG of a rabbit before and after surgery. (G) Comparison of hemostatic speed between CS2/TA1/SF1 hydrogel and previously-reported hemostatic dressings.
三、资助信息
上述工作得到国家自然科学基金(Grant No 51903050)、福建省自然科学基金(Grant No. 2019J01258)、高分子材料科学工程国家重点实验室(四川大学)开放课题项目(Sichuan University, Grant No. sklpme2019-4-34)、清源创新实验室重点项目和福州大学贵重仪器设备开放测试基金(2021T025)的资助与支持。
四、原文信息
A mussel-inspired supramolecular hydrogel with robust tissue anchor for rapid hemostasis of arterial and visceral bleedings
Ziwen Qiao a, Xueli Lv c, Shaohua He d, Shumeng Bai c, Xiaochen Liu b, Linxi Hou a, Jingjing He a, Dongmei Tong b, Renjie Ruan a, Jin Zhang a,*, Jianxun Ding e,**, Huanghao Yang b,***
a Qingyuan Innovation Laboratory, College of Chemical Engineering, Fuzhou University, 2 Xueyuan Road, Fuzhou, 350108, PR China
b MOE Key Laboratory for Analytical Science of Food Safety and Biology, State Key Laboratory of Photocatalysis on Energy and Environment, College of Chemistry, Fuzhou University, 2 Xueyuan Road, Fuzhou, 350108, PR China
c College of Biological Science and Engineering, Fuzhou University, 2 Xueyuan Road, Fuzhou, 350108, PR China
d Department of Pediatric Surgery, Fujian Provincial Hospital, 134 Dongjie Road, Fuzhou, 350001, PR China
e Key Laboratory of Polymer Ecomaterials, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 5625 Renmin Street, Changchun, 130022, PR China
Bioactive Materials 6 (2021) 2829−2840





 闽公网安备35050502100027
闽公网安备35050502100027